Key words:immunoglobulin, coombs test, hemolysis, HIV, quantification
Introduction
A positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT, Coombs test) is valuable in identifying the etiology of autoimmune hemolysis and in guiding an immunomodulatory therapeutic intervention strategy. However, in HIV positive individuals with background polyclonal gammopathy, a false positive DAT is common. In this setting, immunoglobulin quantification and subtyping may be of value in characterizing the autoimmune hemolysis. There is paucity of published literature evaluating the diagnostic usefulness of IgG subtyping and quantification in HIV positive individuals who are investigated for possible autoimmune haemolysis (AIHA). The recently introduced gel card used for AIHA diagnosis can subtype and quantify the IgG antibody titre. This study evaluated the usefulness of IgG quantification and subtyping in the diagnostic workup of autoimmune hemolysis in patients who were DAT positive with and without HIV infection.
Methods:
This retrospective, cross sectional study was reviewed and approved by the institutional Ethics Committee. The study population included HIV positive and HIV negative patients who were investigated for autoimmune hemolysis in a quaternary care hospital as part of their diagnostic workup. Those with a positive DAT had their IgG subtyped and quantified using the ID -Card DAT IgG1/IgG3 and IgG-dilution cards (Bio-Rad©, Cressier, Switzerland).
Results:
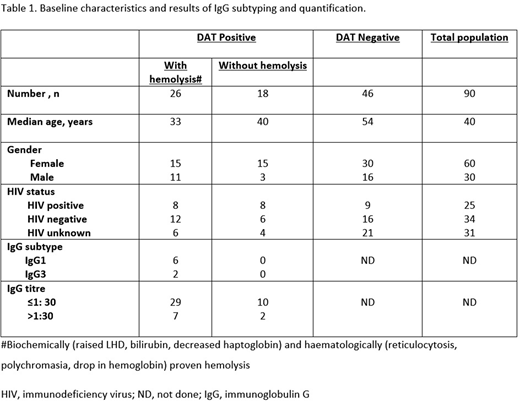
From December 2019 to March 2020, 90 patients admitted in our hospital were investigated for AIHA. Forty four (49%) were found to be DAT positive. Of those who were DAT positive, 26 (59%) had biochemical evidence of haemolysis (raised LDH, raised unconjugated bilirubin). Of the total DAT positive population, 16 (36%) were HIV positive. Concurrent HIV and haemolysis was present in 8 patients. Four of the 8 had antibody titre≤1:30. Most patients had IgG 1 subtype. None of the HIV positive patients without features of haemolysis had IgG1 or IgG3 subtypes present and 2 of the 8 had antibody titres≤1:30.
Conclusion:
IgG quantification and subtyping was found to be of limited value in the diagnostic characterization of AIHA in HIV positive patients with false positive DAT.
Mahlangu:CSL Behring, Catalyst Biosciences, Freeline Therapeutics, Novo Nordisk, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Sanofi, Spark and Takeda:Consultancy;CSL Behring, Catalyst Biosciences, Novo Nordisk, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Sanofi, Spark and Takeda:Speakers Bureau;South Africa Medical Research Council, Wits Health Consortium, Colleges of Medicine of South Africa:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;BioMarin, CSL Behring, Freeline Therapeutics, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, uniQure:Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal